We’re going to talk about the difference between a hub, a switch and a router. All three of these devices are similar, but there is a difference in the way they handle data.
Hub
The purpose of a hub is to connect all of your network devices together on an internal network. It’s a device that has multiple ports that accepts Ethernet connections from network Devices. Hub is considered not intelligent because it does not filter any data nor it has any knowledge as to where the data is supposed to be sent.
The only thing a hub knows is when a device is connected one of its ports. So when a data packet arrives at one of the ports it is copied to all of the other ports and all the devices on that hub sees that data packets. In our example, we have a PC, printer and a laptop connected to a hub. Let’s say that a PC wants to communicate with the printer.
We can see that a data packet from PC comes into the hub which just rebroadcasts that data to every port that has a device connected to it. The data packet is received by the printer and the laptop, even if the PC only wanted to communicate with the printer.
We can see that this not only creates security concerns, but it also creates unnecessary traffic on the network which wastes bandwidth.
Switch
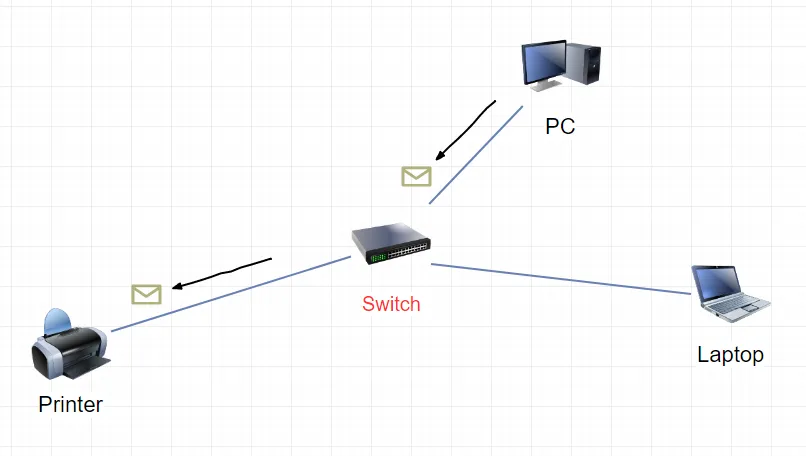
Switch is similar to a hub since since it that has multiple ports that accepts Ethernet connections from network devices, but unlike a hub, a switch is intelligent.
Switch can learn the physical addresses (MAC addresses) of the devices that are connected to it and it store them in a table. When a data packet is sent to a switch, it’s only directed to the intended destination port, while a hub would just rebroadcast the data to every port. So if a PC communicates with the printer using a switch, the data packet arrives at the switch which looks at its table of MAC addresses and matches the exact port to deliver the data to the printer.
So the data only arrives at the intended destination. That’s the major difference between a hub and a switch. Switches are far more preferred over hubs because they reduce any unnecessary traffic on the network and make things more secure.
To review, a hub only detects that a device is physically connected to it, while a switch can detect specific devices by keeping a record of the MAC addresses of connected devices.
Both hubs and switches are used to exchange data within a local area network, for example in home network or in a business network. They are not used to exchange data outside their own network, such as out on the Internet. To exchange (or to route) data outside their own network, to another network such as out on the Iinternet, a device needs to be able to read IP addresses. Hubs and switches do not read IP addresses, so that’s where the router comes in.
Router
Router does exactly what its name implies. Router is a device that routes, or forwards, data from one network to another based on their IP address. When a data packet is received from the router, the router inspects the IP address in data packet, and determines if the packet was meant for its own network or if it’s meant for another network. If the router determines that the data packet is meant for its own network, it receives it. But if it’s not meant for its own network it sends it off to another network.
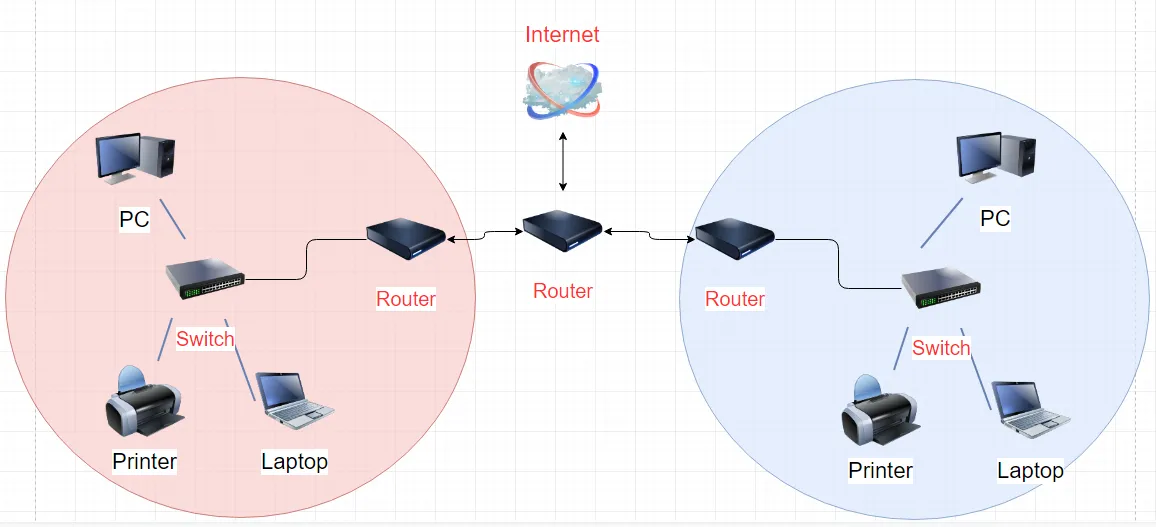
So a router is essentially the gateway of a network. Let’s say that we have two private networks with its routers (red and blue).
If a PC in a red network sends data packet to a printer in the same (red) network, data packet would go to the switch and the switch would direct the packet to the printer. The packet would not even go to the router.
If the PC in the red network wants to communicate with the printer in the blue network, the data packet would have to leave the local (red) network. In typical network configuration, each device will have a designated default gateway for data which is intended for hosts on another network. Because of that, the PC will direct the data packet to the router, since the data is intended for host on another network.
So the computer sends their data, the data goes to the switch which then sends it to the router. Once the data packet reaches the router, the router will look at the IP address of the data packet and then forward the data out to the next router. In that way, the data will make its way to the blue networks router and then to the intended destination. In a nutshell, this is how routers work. If you are in a search for new router, here is a list of routers under 100 dollars.
To conclude, hubs and switches are used to create local networks, while routers are used to connect different networks.