Invalid traffic, including bot clicks, accidental taps, and malicious activity, can derail the success of ad campaigns. It not only wastes budgets but also skews analytics, making it harder to evaluate campaign performance.
To combat this issue effectively, you need the right strategies and tools. This guide outlines 12 detailed tips and tools to help identify and reduce invalid traffic, ensuring your campaigns achieve genuine results.
1. Understanding Invalid Traffic Sources
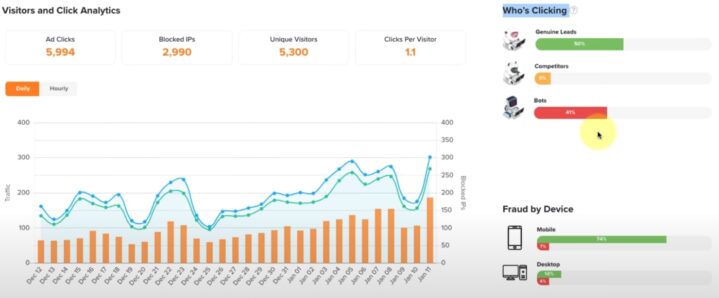
Recognizing the types of invalid traffic is essential to building effective countermeasures. The primary forms include:
- Bot Traffic: Automated systems generating fake clicks or impressions, often designed to inflate metrics artificially.
- Click Farms: Groups of individuals paid to click on ads, often from regions or devices that offer no real business value.
- Accidental Clicks: Occur due to poor ad placement or misleading designs, especially in mobile apps or low-quality websites.
- Malicious Clicks: Intentional activity by competitors or bad actors to drain your ad budget or disrupt performance.
Analyzing traffic sources with tools like Google Analytics or ad network dashboards can help identify patterns indicating invalid activity. Identifying these origins allows you to take targeted actions, such as excluding problematic sources. To enhance your understanding of automated solutions, you can read more about click fraud tools, which use algorithms to detect and mitigate invalid traffic.
2. Reviewing Sources and Engagement
Invalid traffic often originates from untrustworthy or irrelevant sources. Examine your traffic sources in detail to identify anomalies. For example:
- If a single referrer drives a disproportionate volume of clicks with low engagement, it may indicate click farms or bots.
- Sources with exceptionally high bounce rates and short session durations should be flagged for further investigation.
Use filters in analytics tools to focus on specific referrers or campaign elements to uncover problematic trends.
3. Monitoring Click-Through Rates
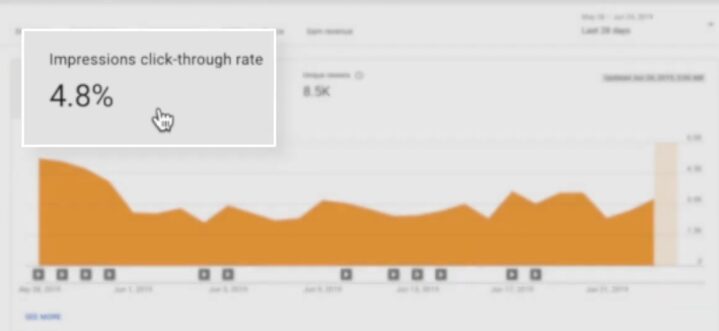
An unusually high click-through rate (CTR) may seem positive at first, but it can signal fraudulent activity. Bots or incentivized clicks often inflate CTR, while real users typically show a balanced ratio between clicks and conversions.
Compare CTR with other engagement metrics such as time on site, pages viewed per session, and bounce rate. A high CTR accompanied by poor engagement indicates invalid traffic that is not converting into meaningful interactions.
4. Analyzing Geographic Data
Geographic discrepancies are a common red flag for invalid traffic. When your campaign targets specific regions, traffic from unexpected locations is a sign of potential fraud. For example:
- Clicks from countries or regions that do not align with your target market can signal bot traffic or click farms.
- Areas with high click volumes but no conversions should be investigated further.
Analytics tools allow you to segment traffic by location, enabling you to pinpoint problematic regions and take corrective actions, such as excluding them from your campaigns.
5. Using IP Exclusions
Blocking problematic IP addresses is a direct way to address known sources of invalid traffic. Ad platforms like Google Ads offer IP exclusion lists, allowing you to prevent clicks or impressions from these addresses.
Regularly review your analytics data to identify IPs associated with suspicious activity. Keep your exclusion lists updated to protect your campaigns from recurring invalid traffic.
6. Setting Frequency Caps
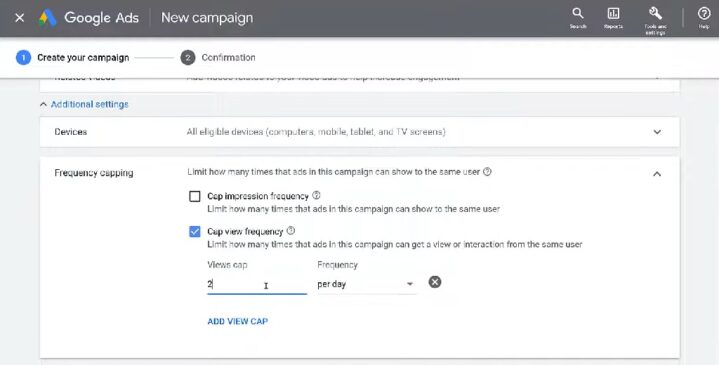
Frequency caps limit the number of times an ad is shown to a single user within a specified time frame. They can mitigate repetitive clicks, particularly in cases where bots or competitors repeatedly click on ads.
By implementing frequency caps, you ensure that ads are not over-served, reducing the likelihood of invalid engagement. This approach also enhances user experience by preventing ad fatigue.
7. Tracking Conversion Metrics
Invalid traffic often manifests as high click volumes but low conversion rates. Tracking conversions is critical to determining whether the traffic you are paying for is generating real results.
Incorporating a tool like the RedTrack tracking platform allows for more precise monitoring of conversions and traffic sources, helping to detect and filter out invalid traffic effectively.
Compare conversion metrics with your expected benchmarks. If conversions are disproportionately low relative to clicks, investigate the sources of traffic to identify potential invalid activity.
8. Leveraging Click Fraud Detection Tools
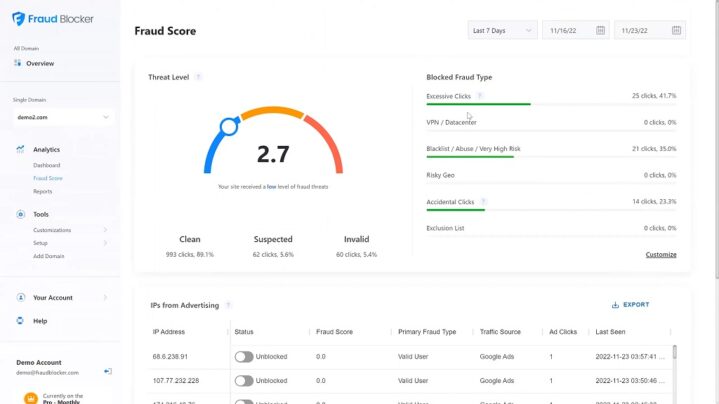
Investing in specialized tools is one of the most effective ways to combat invalid traffic. These platforms analyze data in real-time, identifying patterns indicative of fraudulent behavior.
Some popular tools include:
- ClickCease: Blocks fraudulent clicks and provides detailed reports on invalid activity.
- PPC Protect: Focuses on safeguarding pay-per-click campaigns by identifying malicious behavior.
- Fraud Blocker: Detects suspicious activity and automatically excludes problematic sources.
These tools often integrate directly with ad platforms, providing seamless protection for your campaigns.
9. Monitoring Device and Browser Data
Invalid traffic often comes from devices or browsers that deviate from normal user behavior. For instance:
- A spike in clicks from outdated browsers may indicate bot activity.
- Unusual patterns in screen resolutions, operating systems, or device types can also signal automated clicks.
Regularly analyze device and browser data to identify trends that do not align with your target audience.
10. Reviewing Ad Placement Data
Ad placements play a significant role in traffic quality. Ads placed on low-quality websites or apps with poor design often result in accidental or fraudulent clicks.
Conduct placement audits to identify where your ads are appearing. Look for placements with high impressions but low engagement, as these often attract invalid traffic. Adjust your targeting settings to focus on reputable websites aligned with your campaign objectives.
11. Setting Up Advanced Targeting
Advanced audience targeting helps reduce exposure to invalid traffic. Narrow your audience based on precise demographics, geographic regions, and user interests. Exclude broad categories that may attract low-quality or irrelevant clicks.
For example:
- Focus on regions with high conversion rates and proven engagement.
- Use remarketing lists to target users who have already shown interest in your brand.
This ensures that your ads reach users most likely to convert, reducing the impact of invalid traffic.
12. Conducting Regular Campaign Audits
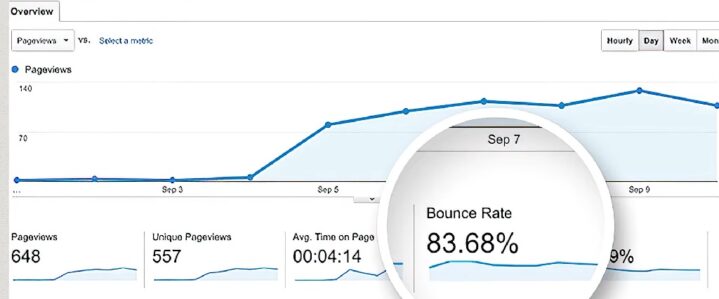
Regularly reviewing campaign performance helps detect invalid traffic early. Use key metrics like CTR, conversion rates, and bounce rates to identify inconsistencies. Audits should include:
- Reviewing traffic sources for anomalies.
- Checking geographic and device data for irregular patterns.
- Analyzing ad placement reports to ensure quality exposure.
Frequent audits provide the opportunity to make adjustments before invalid traffic significantly impacts your campaign.
Closing Thoughts
Invalid traffic remains a persistent challenge for advertisers, but with the right strategies and tools, it can be effectively managed. By understanding the types of invalid activity, monitoring key metrics, and leveraging advanced detection tools, you can protect your campaigns from fraud and optimize your ad spend. Safeguarding your campaigns ensures that your efforts deliver genuine results and meaningful engagement.
